Incorporating Technology into Physical Education: Enhancing Engagement and Learning

The Benefits of Technology in Physical Education
Enhancing Student Engagement
Technology has the potential to increase student engagement in PE. Interactive apps, gamified fitness programs, and wearable devices can motivate students to participate in physical activities and track their progress in real-time. By introducing elements of play and competition, these tools turn physical fitness into an exciting and enjoyable experience (Papanastasiou et al., 2019).
Personalized Learning Experiences
Technology allows for a more individualized approach to PE. Fitness trackers and mobile apps enable students to monitor their performance, set personalized goals, and track progress based on their unique fitness levels, abilities, and interests. This personalized feedback fosters a sense of accomplishment and empowerment (Martin & Hultman, 2022).
Improved Understanding of Complex Movements
Virtual reality (VR) simulations enhance students' comprehension of intricate movements and skills. Research has shown that VR training can be as effective as traditional video training in helping students acquire complex sports movements. By providing immersive 3D experiences, VR enables students to visualize and practice physical activities in a controlled environment, facilitating skill development and knowledge retention (Pastel et al., 2022).
Enhanced Spatial Awareness and Coordination
The use of 3D virtual environments in PE classes improves students' spatial awareness and movement coordination by 36%. These technologies allow students to engage with dynamic simulations, aiding in developing essential motor skills and spatial understanding (Pastel et al., 2022).
Exploring the Integration of Virtual Reality in Physical Education
Research indicates that VR-based interventions can improve student performance, knowledge retention, and adherence to exercise programs by providing immersive and realistic learning experiences. These studies highlight the effectiveness of VR in delivering experiential learning opportunities (Pastel et al., 2022).
Access to Health and Fitness Information
Technology provides students with immediate access to a wealth of resources on health, nutrition, fitness, and sports. Research indicates that instructional videos, fitness apps, and online tutorials can facilitate learning about different exercises, sports techniques, and rules. Studies have found that using video tutorials significantly improved physical fitness levels among physical education students compared to traditional methods (Al-Haliq et al., 2013). Additionally, video tutorials with attractive and easy-to-understand visuals have been shown to increase student motivation and improve basic motor skills, such as running, jumping, and throwing (Panjiantariksa, 2024). Studies have found that these digital resources enhance students' understanding and application of physical activities by providing structured guidance and real-time feedback (Yau et al., 2022).

Challenges and Considerations
Ensuring Technological Inclusivity
While technology can enhance learning, it is crucial to ensure that all students, including those with disabilities or special needs, can access and benefit from these tools. Selecting technologies with built-in accessibility features and providing alternative methods or adaptations can help create a more inclusive PE environment (Villumis, 2024). However, it is important to verify the effectiveness of these tools through empirical studies or case studies on their impact (Pastel et al., 2022).
Managing Technology Overload
Simultaneously introducing multiple new technologies can overwhelm both students and educators, potentially reducing the effectiveness of PE programs. A gradual integration plan, accompanied by adequate training and support, ensures effective utilization of technological tools (Villumis, 2024; Pastel et al., 2022).
Evaluating Technology Effectiveness
Assessing the impact of technology on student learning and physical development is essential for informed decision-making. Establishing clear evaluation criteria and regularly collecting feedback can help educators determine the effectiveness of technological tools and make necessary adjustments to enhance learning outcomes (Villumis, 2024; Pastel et al., 2022).
Balancing Screen Time
The use of technology in PE may increase students' screen time, potentially leading to more sedentary behavior. Teachers must balance technology use with physical movement to ensure that it enhances rather than detracts from PE (Yau et al., 2022).
Real-World Examples of Technology in Physical Education
Innovative Training Methods
Elite soccer clubs, such as Leeds United and Sunderland AFC, have adopted training in specially designed darkened environments to enhance players' visual motor skills. The website Wired published a post based on this innovative approach, which has led to significant improvements in players' reaction times and accuracy, demonstrating the potential of creative technological applications in sports training (Rodrigues et al., 2024).
Community Engagement through Technology
The "bike bus" movement, revitalized by Sam Balto in Portland, Oregon, showcases how technology and social media can promote physical activity. By organizing group cycling events and sharing them online, this initiative encourages communities to engage in regular physical activity, highlighting the role of technology in fostering active lifestyles (The Guardian, 2025).
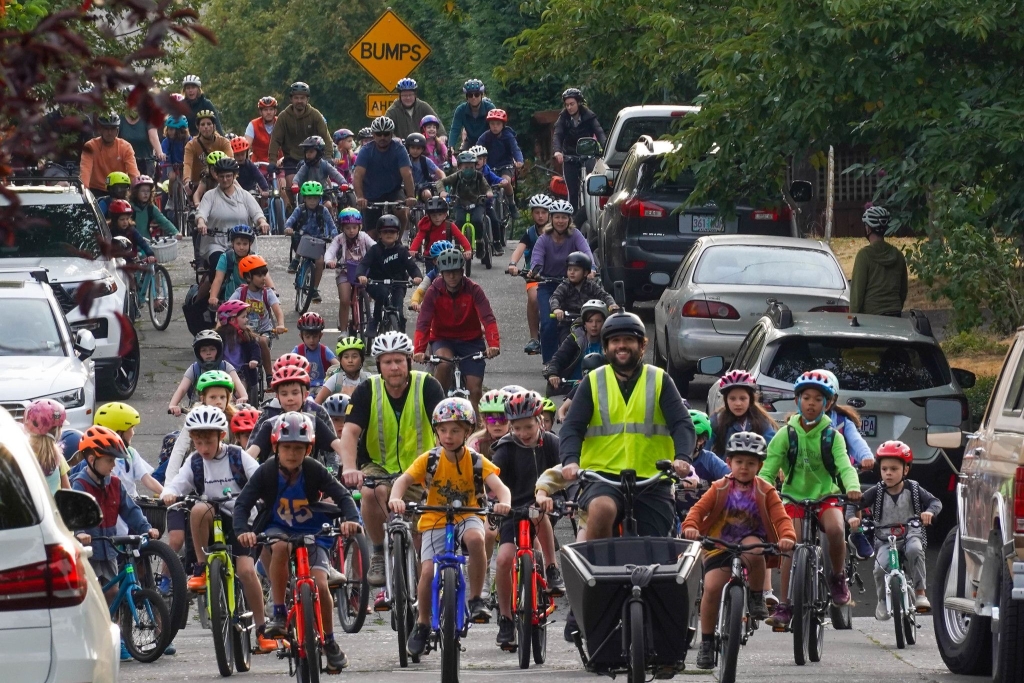

Photo: Sam Balto leading his Bike Bus (Ling, 2023).
Conclusion
Technology has the potential to significantly enhance the learning experience in physical education, offering numerous benefits such as increased engagement, personalized learning, access to information, and more inclusive practices. Through the use of wearable fitness trackers, virtual reality simulations, and interactive apps, students can take a more active role in their fitness journeys by tracking progress and setting personalized goals. Additionally, technology allows for real-time feedback, enabling educators to adjust instruction based on student performance and engagement. However, its implementation must be carefully considered to avoid challenges such as cost, increased screen time, and potential distractions. Schools should develop structured integration plans that include teacher training, clear technology use guidelines, and periodic effectiveness assessments. By thoughtfully incorporating technology and balancing it with traditional physical activities, educators can create a dynamic, inclusive, and effective PE environment that meets the evolving needs of students.
References
Al-Haliq, M. A., Oudat, M. A., & Al-Taieb, M. A. (2013). The effect of using video on developing physical fitness of physical education students at the Hashemite University. Asian Social Science, 10(1). https://doi.org/10.5539/ass.v10n1p21
Ling, M. (2023, April 7). #BikeBus: Sam Balto is Like the Ringleader for the Coolest Bike Gang Ever. Bicycling. https://www.bicycling.com/news/a43541199/sam-balto-bike-bus/
Martin, N., & Hultman, R. (2022). Applicability of fitness trackers in the physical education of fifth- and Sixth-Grade students. Journal of Physical Education Recreation & Dance, 93(6), 29–34. https://doi.org/10.1080/07303084.2022.2081272
Panjiantariksa, Y. (2024, November 30). Effectiveness of using video tutorials in Physical education learning: case study at MA. https://ejournal.imbima.org/index.php/champions/article/view/304
Papanastasiou, G., Drigas, A., Skianis, C., Lytras, M., & Papanastasiou, E. (2019). Virtual and augmented reality effects on K-12, higher and tertiary education students’ twenty-first century skills. Virtual Reality, 23(4), 425–436. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10055-018-0363-2
Pastel, S., Petri, K., Chen, C. H., Cáceres, A. M. W., Stirnatis, M., Nübel, C., Schlotter, L., & Witte, K. (2022). Training in virtual reality enables learning of a complex sports movement. Virtual Reality, 27(2), 523–540. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10055-022-00679-7
Rodrigues, P., Woodburn, J., Bond, A. J., Stockman, A., & Vera, J. (2024). Light‐based manipulation of visual processing speed during soccer‐specific training has a positive impact on visual and visuomotor abilities in professional soccer players. Ophthalmic and Physiological Optics. https://doi.org/10.1111/opo.13423
The Guardian. (2025, February 20). Cycling to school almost became extinct – until one man revived the bike bus. The Guardian. https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2025/feb/20/cycling-to-school-almost-became-extinct-until-one-man-revived-the-bike-bus
Villumis. (2024, August 29). Transforming Physical Education: The Power of Technology in Theory and Practice – Villumis blog. https://villumis.com/blog/transforming-physical-education-the-power-of-technology-in-theory-and-practice/
Yau, K. W., Tang, T. S., Görges, M., Pinkney, S., Kim, A. D., Kalia, A., & Amed, S. (2022). Effectiveness of mobile apps in Promoting healthy behavior changes and Preventing obesity in Children: Systematic review. JMIR Pediatrics and Parenting, 5(1), e34967. https://doi.org/10.2196/34967