Mindfulness Benefits and Practices for the Classroom

First, what is Mindfulness?
Mindfulness as a word has been around for centuries. In short, Mindfulness is to be present in the moment with all your senses, nonjudgmentally, and not worrying about the past or the future. Presence comes when we are attentive, when we are aware of our experience. Mindfulness really is about “attention and awareness that arises from paying attention on purpose, in the present moment and non-judgmentally” (Kabat-Zinn, 2005, page 4).
Why is this important in schools?
Teachers and students alike are busy in today’s go-go-go world, full of technology, immediate reactions and responses. There are so many distractions, it can be hard to focus and concentrate on being in the moment. Mindfulness teaches us to come back to the present, to self-regulate emotions, especially ones that are difficult to deal with (e.g. anger, anxiety, fear), and to reflect and analyze in a more open way when engaging with others. We can use mindful practices such as breathwork, kindness, gratitude and more to help calm our brains and connect, grounding, thus preventing us from spinning and possibly reacting in a way that we regret later (e.g. aggression) through better decision making. Other benefits of Mindfulness include (but are not limited to):
- Positive classroom atmosphere;
- Better focus and concentration;
- Respect, Kindness, Openness, Acceptance of others and oneself;
- Improved sleep;
- Emotional balance; and
- Enhanced communication.
How can it be done?
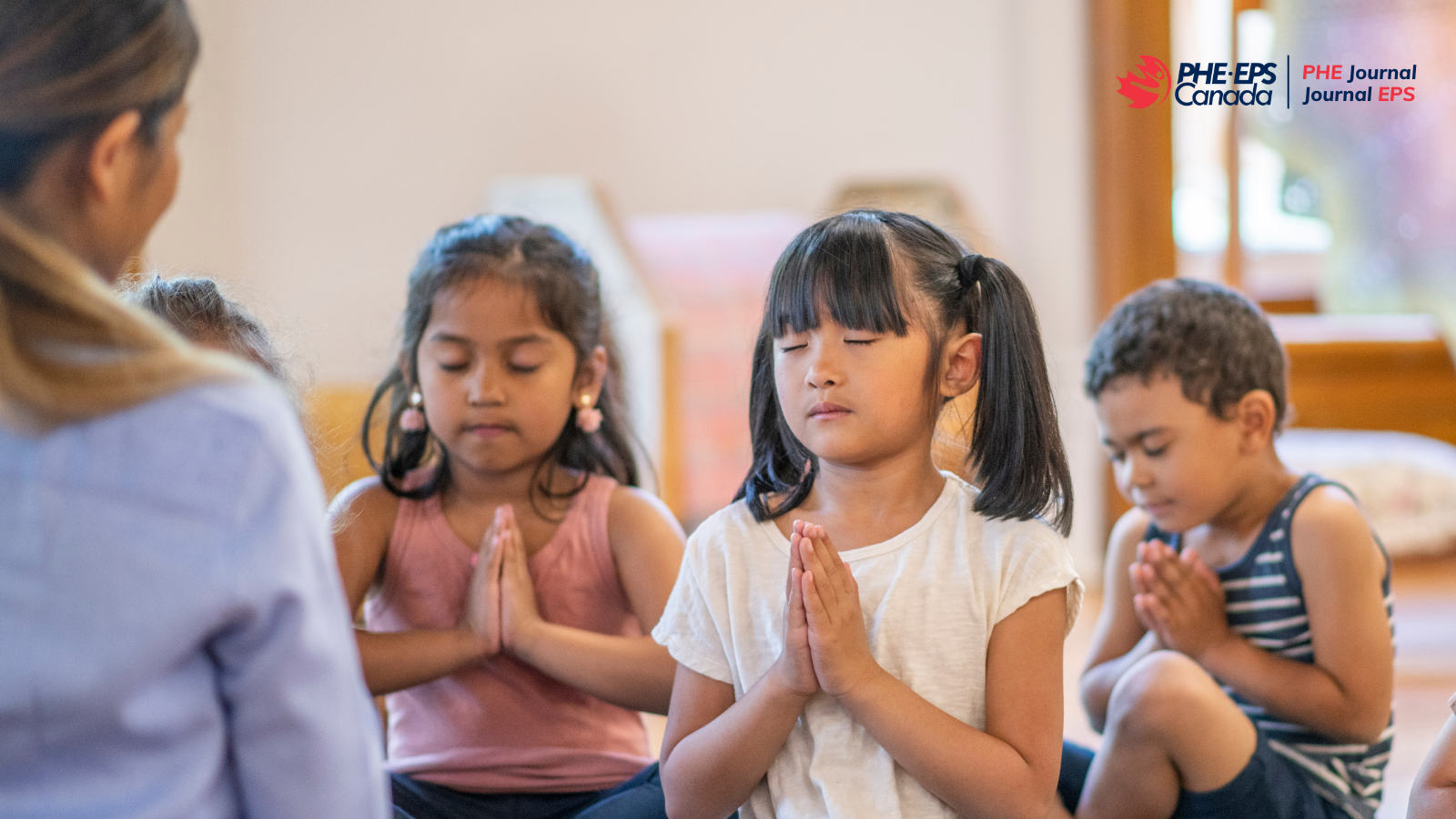
Remodeling our classroom to better support our mental health is not as difficult as one might think. A few simple tools to bring into our own life will transform our classrooms into a safer place to be present, encouraging our students to show up as their authentic selves. Too often we want a quick fix like ‘Mindful Mondays’, and although this is a great place to start, it doesn’t always carry through the rest of the week. Mindfulness requires practice, and consistency is key. It does not need to be time consuming or interfere with our instructional time as we can start an informal practice with as little as 5 minutes at a time. The more we, as teachers, practice mindfulness, the more our classrooms will become a mindful environment and modeling this practice with our students is important.

3 Mindfulness Activities to start with your class
- COUNTING BREATH MEDITATION: Start each class with 2-3 minutes of counting your breath. Set a timer for your desired time or start small with a 1 minute timer and then work your way up. Introducing the breath. Inhale through your nose for a count of 3 and exhale through your mouth or nose for a count of 3. If your mind wonders, come back to the numbers. Counting our breath gives our mind something to do.
- 5,4,3,2,1………..SENSE Meditation: Have students notice 5 things they see. Ask them to focus on the shape, color, tone. Get each to be curious in their noticing. A curious mind is less judgemental and more open. Then, ask students to notice 4 things they hear, focussing on the volume, tone, frequency. Next, have students focus on 3 things they feel, notice the feeling of their clothes on their skin, hands on the table, hair ect. Guide students to think about whether it is soft, fuzzy, rough ect. Next, notice 2 things they smell. Feel the air at the tips of nostrils, follow the airflow, notice a smell. Finally, ask students to notice 1 thing they taste. Notice the tip of tongue, the sides, the back of the tongue. While students are doing this, encourage them to bring their attention back to the sense meditation and focus on their breathing. Being present is important.
- BODY SCAN: This type of meditation will help students with anxiety by allowing them to ground into their body. It can be very helpful before exams, tests or big events. Have the students sit anywhere in the classroom that is comfortable for them. Have students first focus on their breath, similar to the ‘Counting Breath Meditation’. Next, choose a part of the body for students to focus their attention on, noticing all the feelings and sensation (i.e., the right foot). Continue this until you’ve scanned the entire body. Start small by scanning each foot, each leg, the hands, arms, and so on. To get you started with scanning your body, check out this script from Anxiety Canada to take you through this practice.
In my experience, once these informal practices are in place in our classrooms students really enjoy them, will notice if they are missing, and end up running the practices themselves. I invite you to show up for your class. I invite you to show up for yourself. I invite you to choose one of these practices and practice it for 21 days straight and notice the effects it has. It is more important than ever to start showing up in the present and these simple mindfulness activities can help you do that.
References
Kabat-Zinn, J. (2005). Wherever You Go, There You Are: Mindfulness Meditation in Everyday Life (-1st ed., p. 4). Hachette Books.