Health Education (HE) Instructional Considerations: How do we ensure we are responsive to student needs through the health curriculum as a pathway toward creating more effective education?
The health and well-being of young people requires sustained health education and health promoting opportunities throughout the school day. With the return to school, there is a need for this to be well defined and resourced. In planning for optimizing the role of HE in your jurisdiction, guiding principles should include:
Blended learning (online and in school learning)
- Set specific times for online instruction
- Ensure safe, secure, and trusted connections and platforms for use
- Utilize special interest items such as videos, audio recordings, worksheets, quizzes, student activity handouts, and/or textbook readings sequentially throughout the year in a flipped classroom approach
- Ensure that whatever learnings are to be done online are readable and accessible for all students
In school learning
- Ensure dedicated HE instructional time at the elementary and secondary levels
- Focus on functional health knowledge and identifying key skills that are applicable to all aspects of health literacy
- Increase attention and student voice around harmful behaviours, such as tobacco and substance use, addictions, risk taking activities, illegal activities, truancy, and bullying
- Activate students' sense of control by involving students in active, participatory learning experiences, rather than passive ones
- Keep the E in HE through reflection and critical thinking
- Enhance learning through transdisciplinary opportunities, leadership, and school-wide activities throughout the school day
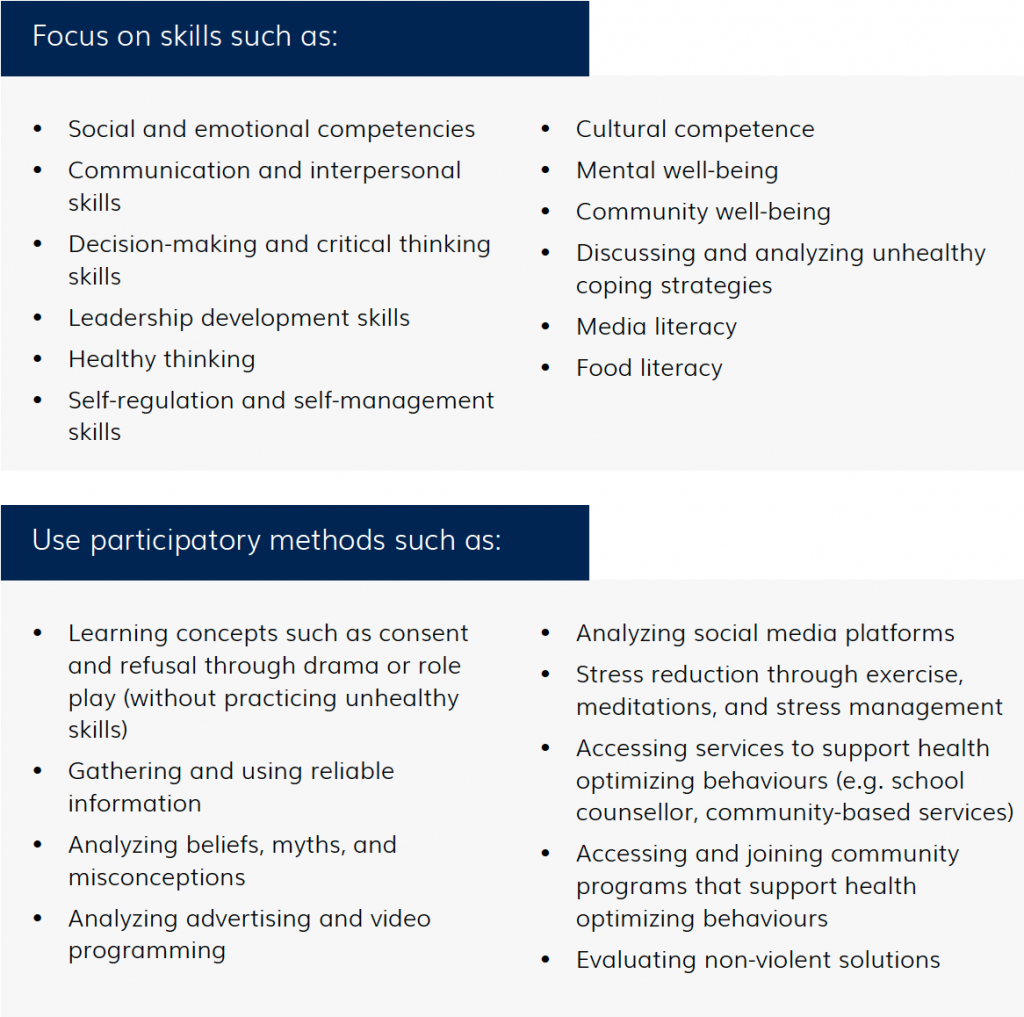
The following chart highlights areas of the health education curriculum that activate students cognitive (think), affective (feel), and behavioural (act) competence. By using the participatory methods on the right, learning can be optimized.